SAT-Cloudlog-Bridge: Log QSOs from S.A.T. directly to Cloudlog/Wavelog
Posted on 2025-09-30 by DK1MIThe CSN Technologies S.A.T. is “a self contained antenna rotator and radio controller” which “natively controls Icom radios, Yaesu rotators and can interface with PSTRotator. The S.A.T. works with any modern web browser on any device.” This device is also capable of logging contacts directly from within its web interface. These logs are stored on the S.A.T. itself which can be configured to send every log entry to another device/service right after it was created.
As a Cloudlog or Wavelog user, you want to have these logs transferred to your actual logbook. That’s why I developed a Python script that listens on a freely definable port, receives the log entries from the S.A.T. controller there, and then forwards them to a Cloudlog/Wavelog instance. This script can be found here on my GitHub.
The following must be configured on the S.A.T. in the “LOCATION” window:
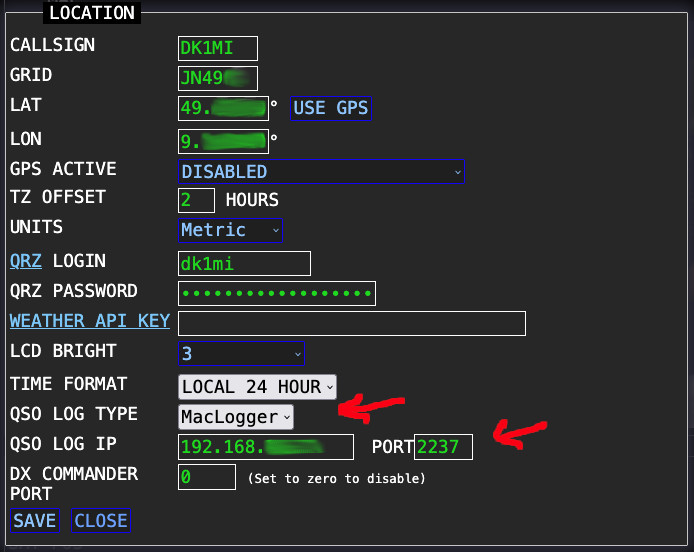
- QSO LOG TYPE: MacLogger
- QSO LOG IP: Enter here the IP address of the system on which the SAT-Cloudlog-Bridge script is running
- PORT: e.g. 2237
The SAT-Cloudlog-Bridge script must then be executed on a system in the network, e.g. a Raspberry Pi. The necessary configuration parameters can be set either within the script or via parameters. If the default port 2237 is retained, the command would look like this:
python3 ./SAT-Cloudlog-Bridge.py --cloudlog-url https://log.dclnext.darc.de --api-key wlxxxxxxxxxxxxx --station-id 123
Of course, you must adapt the parameters to your own Cloudlog/Wavelog instance.
If you now log a QSO within the S.A.T. web interface, it will be automatically forwarded to the configured Cloudlog/Wavelog instance. Most of the entries are then already pre-filled, e.g., the name of the satellite or the RX and TX band and frequency.